미로 생성기 03
개요
남은 알고리즘 미로 추가하여 미로 생성기 완성하기.
구현
시작 전에 길찾고 그리는 부분이 중복되기 때문에 공통 함수로 옮겨줬다.
1. Binary Tree 알고리즘과 Sidewinder 알고리즘
두 알고리즘의 미로 생성 과정이나 결과물은 상당히 유사해보인다.
셀에서 방향을 무작위로 선택해 벽을 제거하고 나아가는 방식이다.
차이점을 정리해보면
- Binary Tree
- 각 셀마다 독립적으로 결정을 내림
- 대각선 방향의 경향
- Sidewinder
- 연속된 동쪽 경로인 run이라는 개념을 활용, 동쪽으로 진행
- 현재 run에서 무작위 셀을 남쪽으로 연결하며 run 종료
- 이전 셀들의 선택이 다음 셀 선택에 영향을 줌
- 수평 방향의 경향
실제 입구 출구를 이어보면 이는 더 명확하게 드러난다.
전통적인 Sidewinder 알고리즘 사용시 동쪽과 북쪽을 선택하는데
시작 좌표를 [0, 0] 으로 잡기 때문에 동쪽과 남쪽으로 진행하게 방향을 잡았다.
// Binary Tree 알고리즘
async function generateBinaryTree() {
// 모든 셀을 벽으로 초기화
for (let y = 0; y < rows; y++) {
for (let x = 0; x < cols; x++) {
maze[y][x] = 1;
drawCell(x, y, 'black');
}
}
// 각 셀에 대해
for (let y = 0; y < rows; y += 2) {
for (let x = 0; x < cols; x += 2) {
// 현재 셀을 통로로 만들기
maze[y][x] = 0;
drawCell(x, y, 'white');
// 동쪽과 남쪽 중 하나를 무작위로 선택
const canGoEast = x + 2 < cols;
const canGoSouth = y + 2 < rows;
if (canGoEast && canGoSouth) {
// 둘 다 가능하면 무작위로 선택
if (Math.random() < 0.5) {
// 동쪽으로
maze[y][x + 1] = 0;
drawCell(x + 1, y, 'white');
} else {
// 남쪽으로
maze[y + 1][x] = 0;
drawCell(x, y + 1, 'white');
}
} else if (canGoEast) {
// 동쪽만 가능
maze[y][x + 1] = 0;
drawCell(x + 1, y, 'white');
} else if (canGoSouth) {
// 남쪽만 가능
maze[y + 1][x] = 0;
drawCell(x, y + 1, 'white');
}
await sleep(5);
}
}
}
// Sidewinder 알고리즘
// 전통적인 Sidewinder 알고리즘은 북쪽으로 길을 파는데 입구가 0,0이라 남쪽으로 파는 것으로 변경
async function generateSidewinder() {
// 모든 셀을 벽으로 초기화
for (let y = 0; y < rows; y++) {
for (let x = 0; x < cols; x++) {
maze[y][x] = 1;
drawCell(x, y, 'black');
}
}
// 각 행을 처리
for (let y = 0; y < rows; y += 2) {
let run = []; // 현재 실행 중인 경로 (연속된 동쪽 경로)
for (let x = 0; x < cols; x += 2) {
// 현재 셀을 통로로 만들기
maze[y][x] = 0;
drawCell(x, y, 'white');
run.push([x, y]); // 현재 셀을 run에 추가
// 동쪽으로 갈 수 있는지 확인
const canGoEast = x + 2 < cols;
// 남쪽으로 갈 수 있는지 확인
const canGoSouth = y + 2 < rows;
// 동쪽으로 계속 진행할지, 남쪽으로 연결할지 결정
// 1. 동쪽으로 갈 수 없거나
// 2. 남쪽으로 갈 수 있고 50% 확률로 run을 종료
const shouldCloseOut = !canGoEast || (canGoSouth && Math.random() < 0.5);
if (shouldCloseOut) {
// 현재 run에서 무작위로 선택된 셀을 남쪽과 연결
const [rx, ry] = run[Math.floor(Math.random() * run.length)];
if (canGoSouth) {
maze[ry + 1][rx] = 0;
drawCell(rx, ry + 1, 'white');
}
run = []; // run 초기화
} else {
// 동쪽으로 계속 진행 (run 확장)
maze[y][x + 1] = 0;
drawCell(x + 1, y, 'white');
}
await sleep(5);
}
}
}
2. Recursive Division 알고리즘
Resursive Division 알고리즘으로 생성된 미로를 보면 다른 미로들과 비교해 상당히 이질적이다.
마치 던전 맵 같은 방 구조로 되어있으며 접근할 수 없는 갇힌 방도 만들어진다.
공간을 분할하며 한 줄짜리 벽을 만들고 벽에 단 하나의 통로만 뚫는다.
이 과정이 반복되며 어떤 영역은 한 통로만 생기고 나머지는 벽으로 막혀버릴 수 있다.
모든 칸이 연결된 완전 미로를 만들기 위해 코드를 약간 수정했다.
벽을 만들 때 이미 통로가 있는지 확인하고 막히게 된다면 추가로 통로를 더 뚫어주는 로직을 넣어주었다.
그래도 막힌 방이 생성됨… 좀 벽을 더 뚫어줘야할 것 같다.
// Recursive Division 알고리즘
// 완전 미로를 만들기 위한 커스텀
// 분할선 크기 조정 시 방 크기 조정
async function generateRecursiveDivision(x1, y1, x2, y2, orientation) {
// 방이 너무 작으면 중단
if (x2 - x1 < 2 || y2 - y1 < 2) {
return;
}
// 수평
if (orientation === 'horizontal') {
// 분할선 후보(짝수)
const possibleYs = [];
for (let y = y1 + 2; y < y2; y += 2) {
possibleYs.push(y);
}
if (possibleYs.length === 0) {
// 분할선 후보가 없으면 중단
return;
}
const y = possibleYs[Math.floor(Math.random() * possibleYs.length)];
// 통로 후보(홀수)
const possiblePassages = [];
for (let x = x1 + 1; x < x2; x += 2) {
possiblePassages.push(x);
}
if (possiblePassages.length === 0) {
// 통로 후보가 없으면 중단
return;
}
// 반드시 하나는 통로로 만들고, 추가로 통로를 더 만들 확률도 부여
const passageCount = 1 + Math.floor(Math.random() * Math.max(1, possiblePassages.length / 3));
const passages = [];
const passageCandidates = [...possiblePassages];
while (passages.length < passageCount && passageCandidates.length > 0) {
const idx = Math.floor(Math.random() * passageCandidates.length);
const px = passageCandidates.splice(idx, 1)[0];
passages.push(px);
}
// 벽 생성 (통로 제외)
for (let x = x1; x <= x2; x++) {
if (!passages.includes(x)) {
maze[y][x] = 1;
drawCell(x, y, 'black');
}
}
await sleep(5);
// 위/아래 영역 재귀 호출
await generateRecursiveDivision(x1, y1, x2, y - 1, 'vertical');
await generateRecursiveDivision(x1, y + 1, x2, y2, 'vertical');
} else { // 수직
// 분할선 후보(짝수)
const possibleXs = [];
for (let x = x1 + 2; x < x2; x += 2) {
possibleXs.push(x);
}
if (possibleXs.length === 0) {
// 분할선 후보가 없으면 중단
return;
}
const x = possibleXs[Math.floor(Math.random() * possibleXs.length)];
// 통로 후보(홀수)
const possiblePassages = [];
for (let y = y1 + 1; y < y2; y += 2) {
possiblePassages.push(y);
}
if (possiblePassages.length === 0) {
// 통로 후보가 없으면 중단
return;
}
// 반드시 하나는 통로로 만들고, 추가로 통로를 더 만들 확률도 부여
const passageCount = 1 + Math.floor(Math.random() * Math.max(1, possiblePassages.length / 3));
const passages = [];
const passageCandidates = [...possiblePassages];
while (passages.length < passageCount && passageCandidates.length > 0) {
const idx = Math.floor(Math.random() * passageCandidates.length);
const py = passageCandidates.splice(idx, 1)[0];
passages.push(py);
}
// 벽 생성 (통로 제외)
for (let y = y1; y <= y2; y++) {
if (!passages.includes(y)) {
maze[y][x] = 1;
drawCell(x, y, 'black');
}
}
await sleep(5);
// 좌/우 영역 재귀 호출
await generateRecursiveDivision(x1, y1, x - 1, y2, 'horizontal');
await generateRecursiveDivision(x + 1, y1, x2, y2, 'horizontal');
}
}
3. Eller’s 알고리즘
Eller’s 알고리즘은 각 행마다 집합을 관리하며 벽을 뚫을 때 집합을 병합하거나 새로 부여한다.
한 줄씩 처리하며 집합 연산과 벽 뚫기만 하고 복잡한 경로 탐색이 없어서 메모리 접근이 효율적이고 엄청나게 빠르다.
실제로 시뮬레이션 돌리면 혼자서 미로를 호다닥 생성해버린다.
엄청나게 빠른게 장점이라면 단점으로는 무작위성이 떨어지며 수평으로 편향되어 있다는 점 정도?
좀 숭숭 뚫려있는 느낌도 받는다.
수직으로 한 칸 짜리 벽 생성을 지양해야하는데 수평으로 한 줄씩 처리하기 때문에 수직 처리하기 곤란하다.
// Eller's Algorithm 미로 생성
async function generateEller() {
// 모든 셀을 벽으로 초기화
for (let y = 0; y < rows; y++) {
for (let x = 0; x < cols; x++) {
maze[y][x] = 1;
drawCell(x, y, 'black');
}
}
// 각 셀의 집합 번호를 저장할 배열
let sets = [];
let nextSet = 1;
// 첫 번째 행 초기화
for (let x = 0; x < cols; x += 2) {
sets[x] = nextSet++;
maze[0][x] = 0;
drawCell(x, 0, 'white');
}
// 각 행을 처리
for (let y = 0; y < rows; y += 2) {
// 1. 오른쪽으로 벽을 뚫을지 결정
for (let x = 0; x < cols - 2; x += 2) {
// 같은 집합이 아니고, 랜덤하게 벽을 뚫기로 결정하면
if (sets[x] !== sets[x + 2] && Math.random() < 0.5) {
// 벽 뚫기
maze[y][x + 1] = 0;
drawCell(x + 1, y, 'white');
// 집합 병합
const oldSet = sets[x + 2];
const newSet = sets[x];
for (let i = 0; i < cols; i += 2) {
if (sets[i] === oldSet) sets[i] = newSet;
}
}
}
// 마지막 행이 아니면 아래로 벽을 뚫기
if (y + 2 < rows) {
// 각 집합별로 아래로 연결할 셀을 최소 1개 이상 선택
const setCells = {};
for (let x = 0; x < cols; x += 2) {
if (!setCells[sets[x]]) setCells[sets[x]] = [];
setCells[sets[x]].push(x);
}
// 아래로 연결
let newSets = [];
for (const set in setCells) {
// 반드시 하나는 아래로 연결
const cells = setCells[set];
const shuffled = cells.slice().sort(() => Math.random() - 0.5);
const downCount = 1 + Math.floor(Math.random() * cells.length);
for (let i = 0; i < downCount; i++) {
const x = shuffled[i];
maze[y + 1][x] = 0;
drawCell(x, y + 1, 'white');
maze[y + 2][x] = 0;
drawCell(x, y + 2, 'white');
newSets[x] = nextSet++;
}
}
// 나머지 셀은 새로운 집합 번호 부여
for (let x = 0; x < cols; x += 2) {
if (!newSets[x]) {
maze[y + 2][x] = 0;
drawCell(x, y + 2, 'white');
newSets[x] = nextSet++;
}
}
sets = newSets;
}
await sleep(10);
}
}
완성
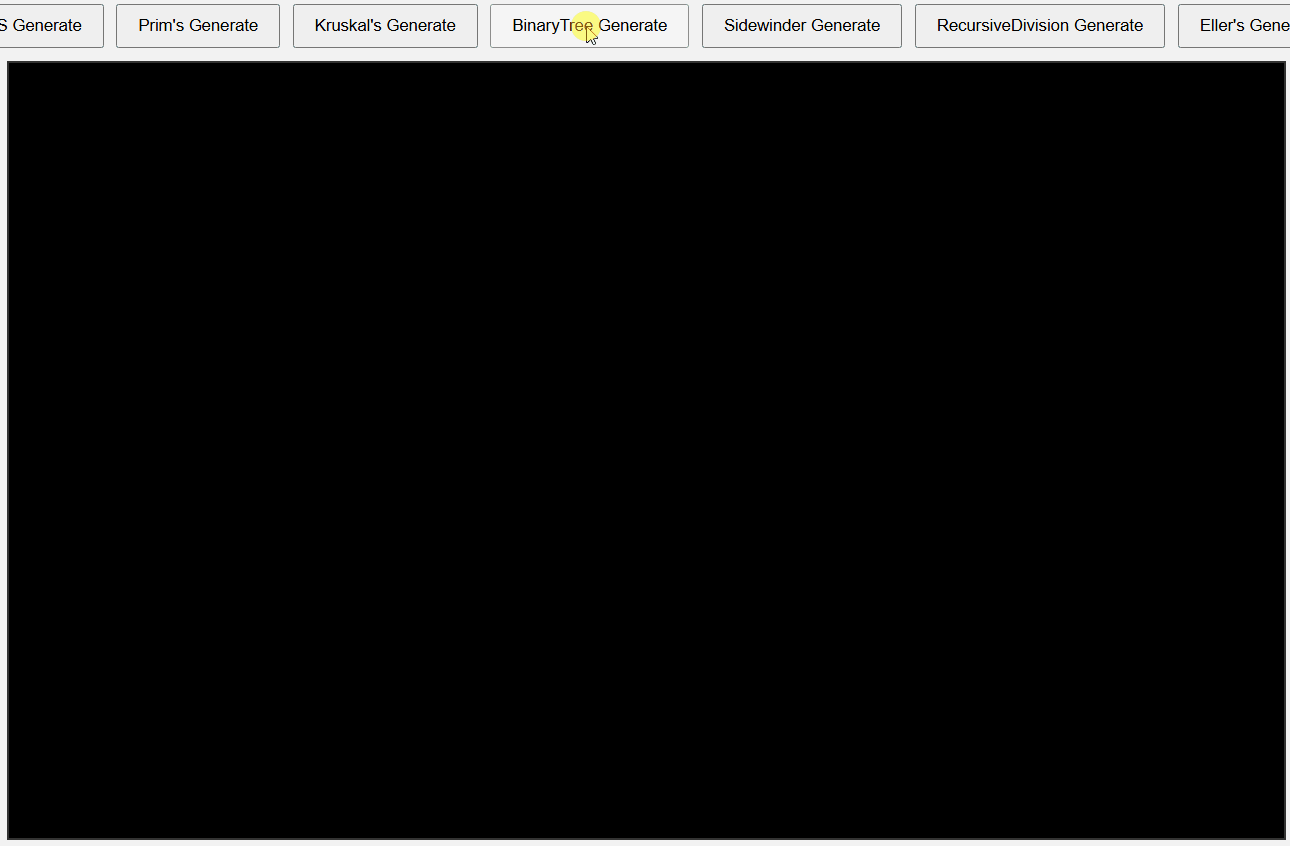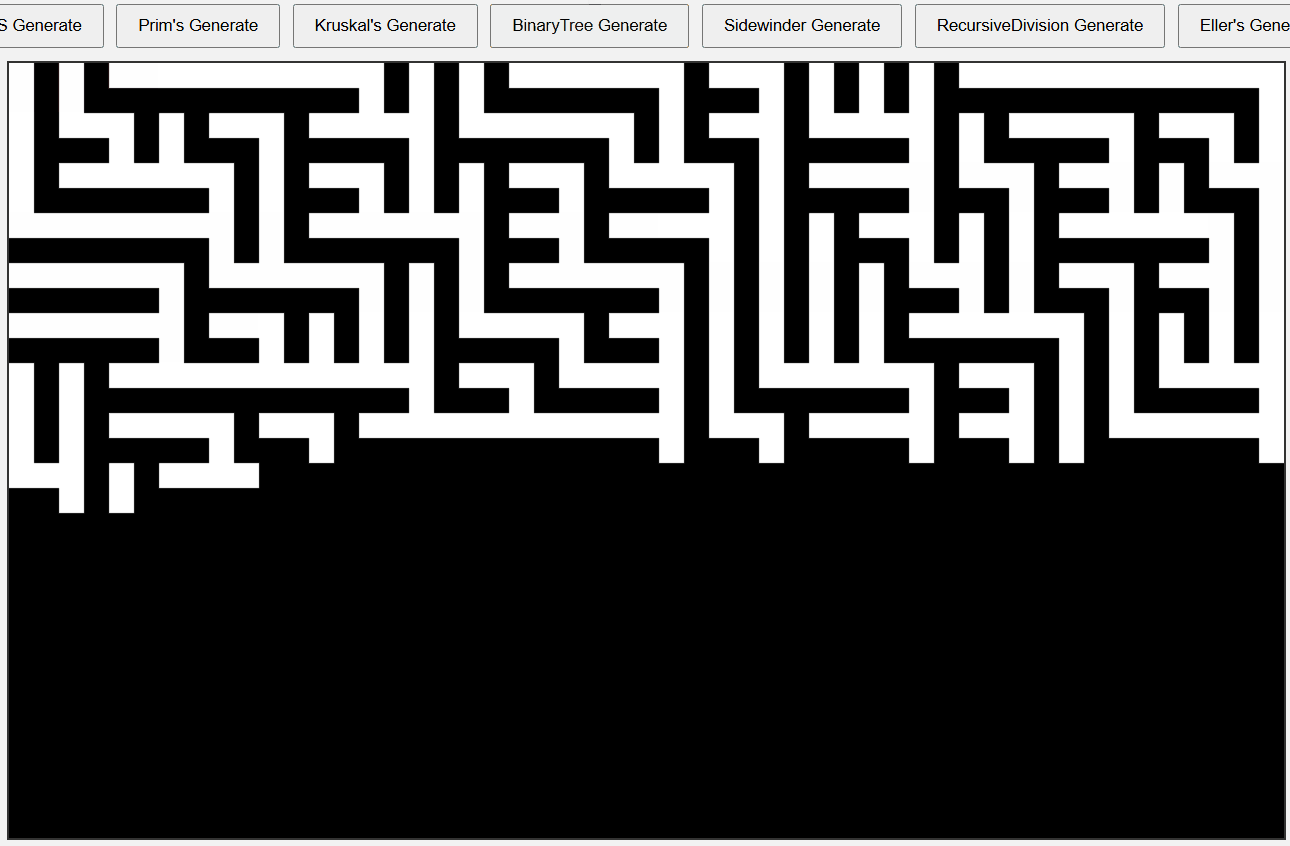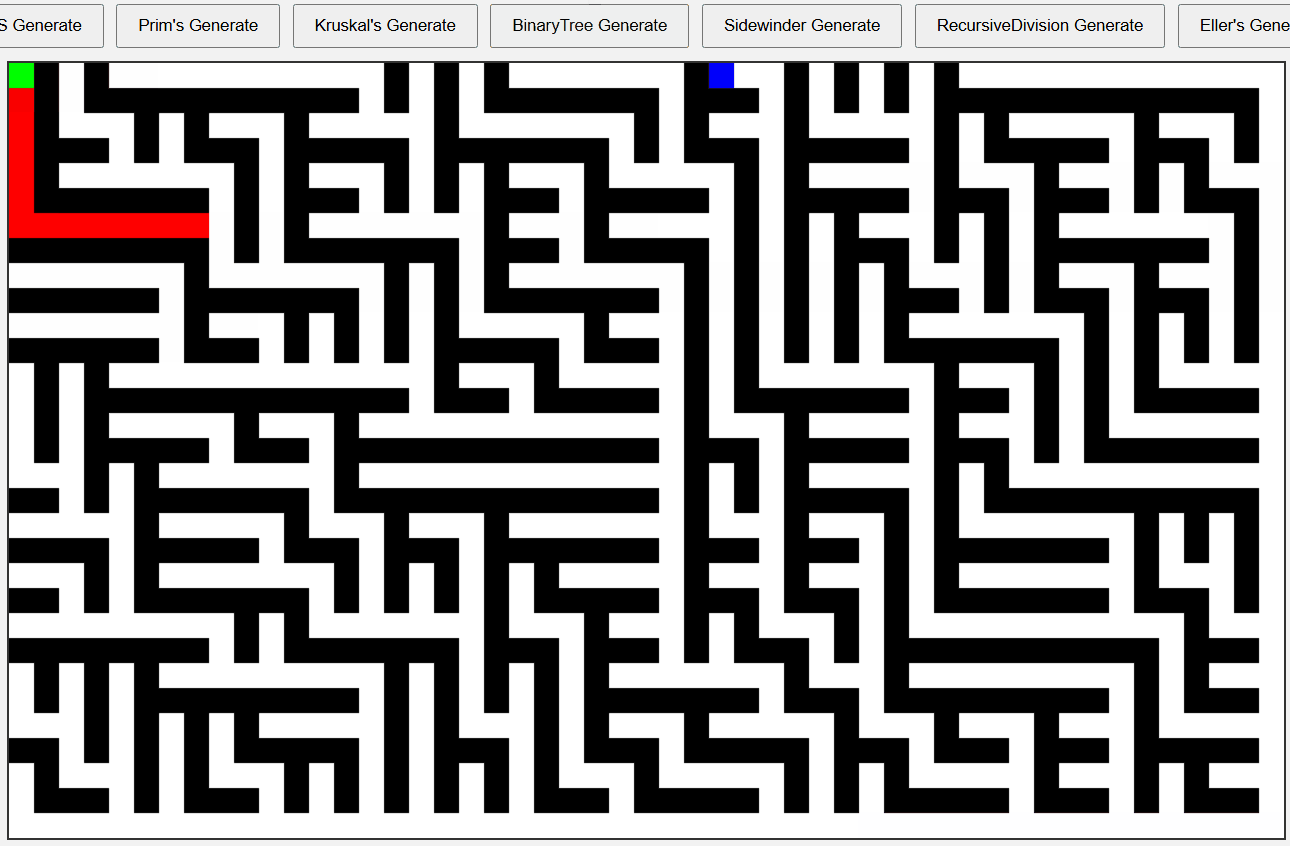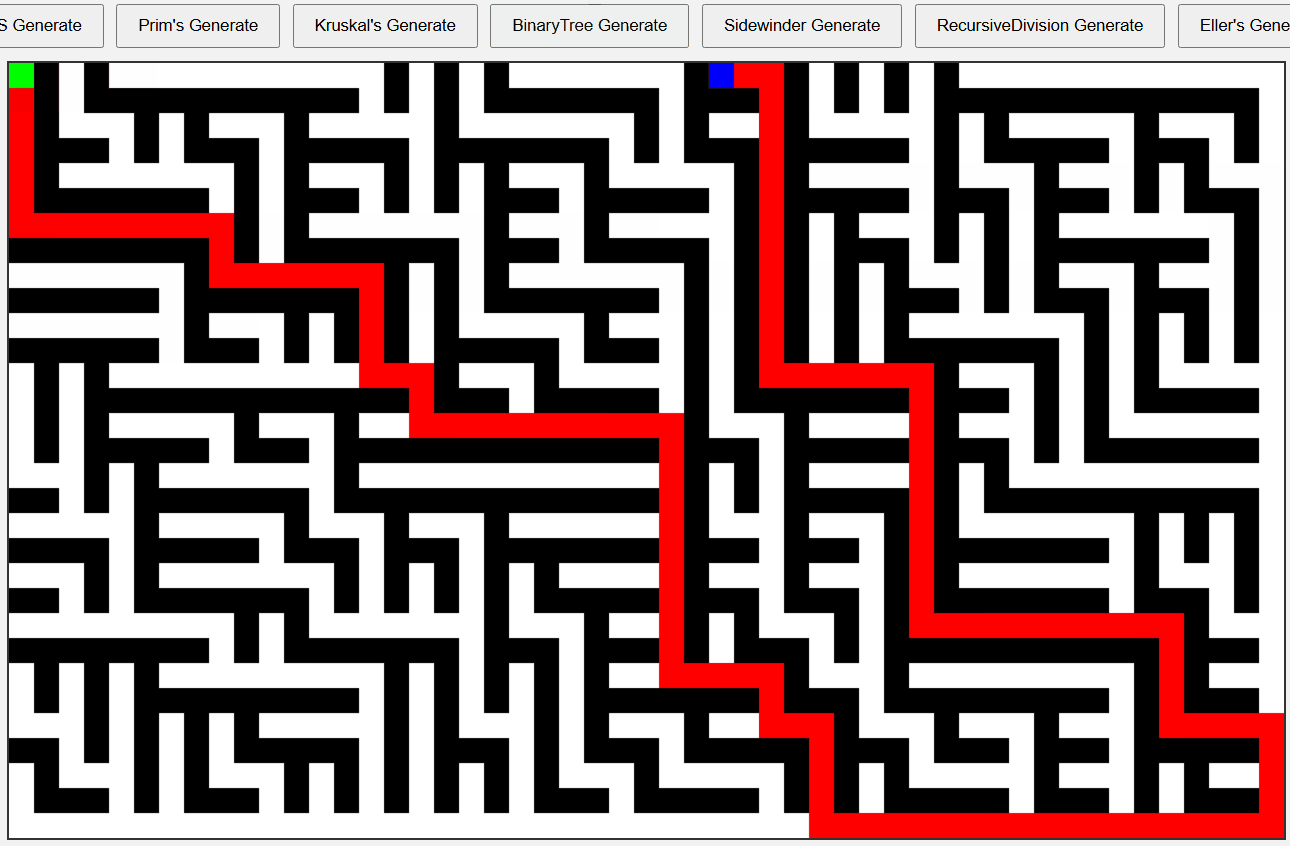
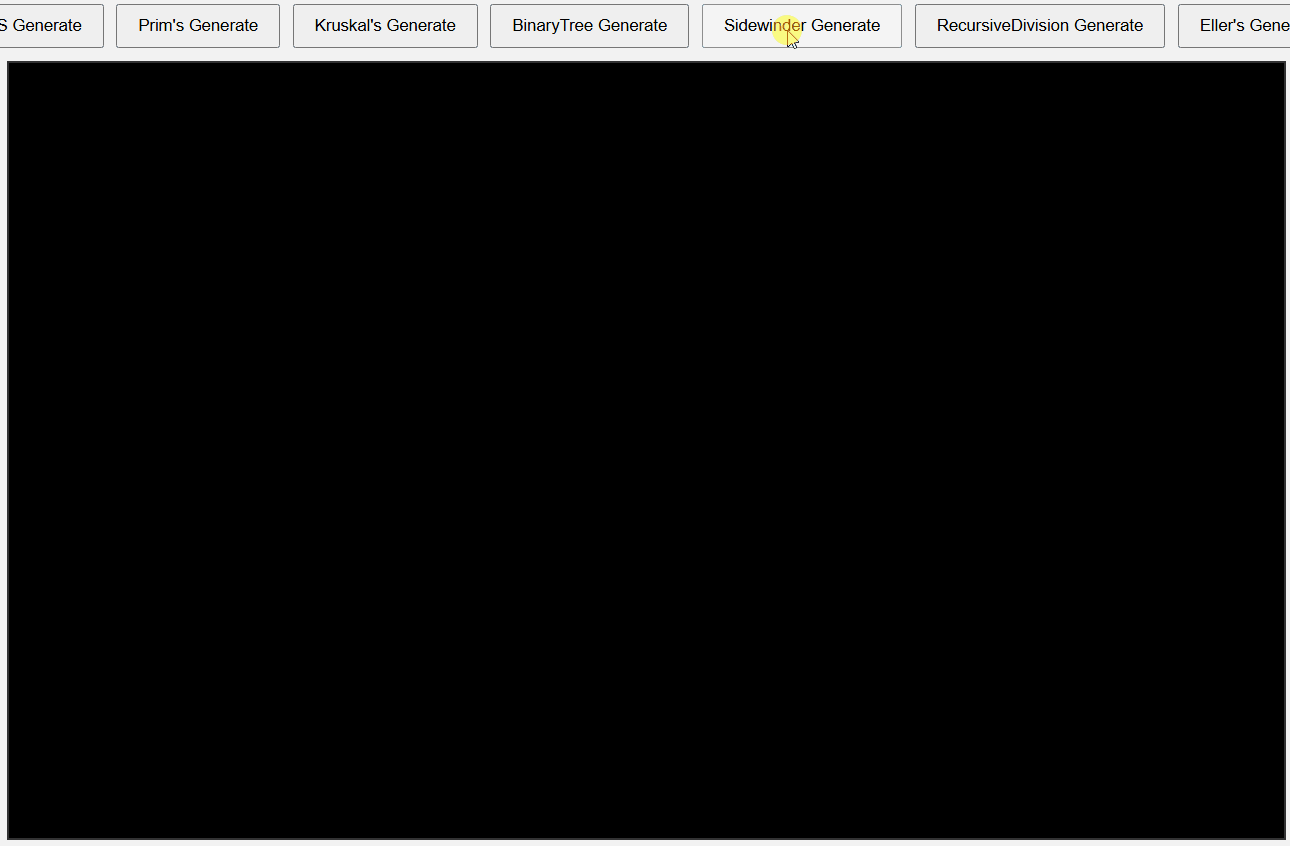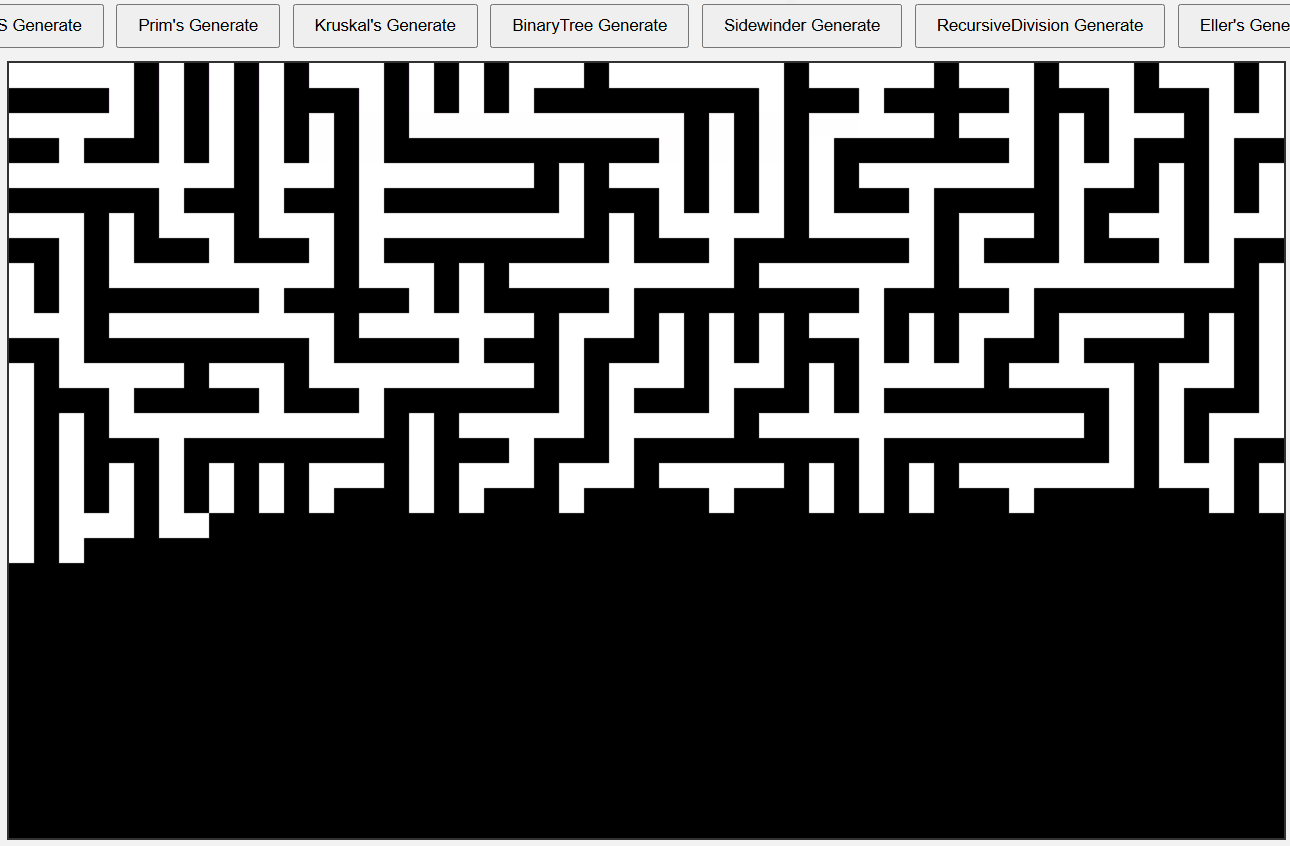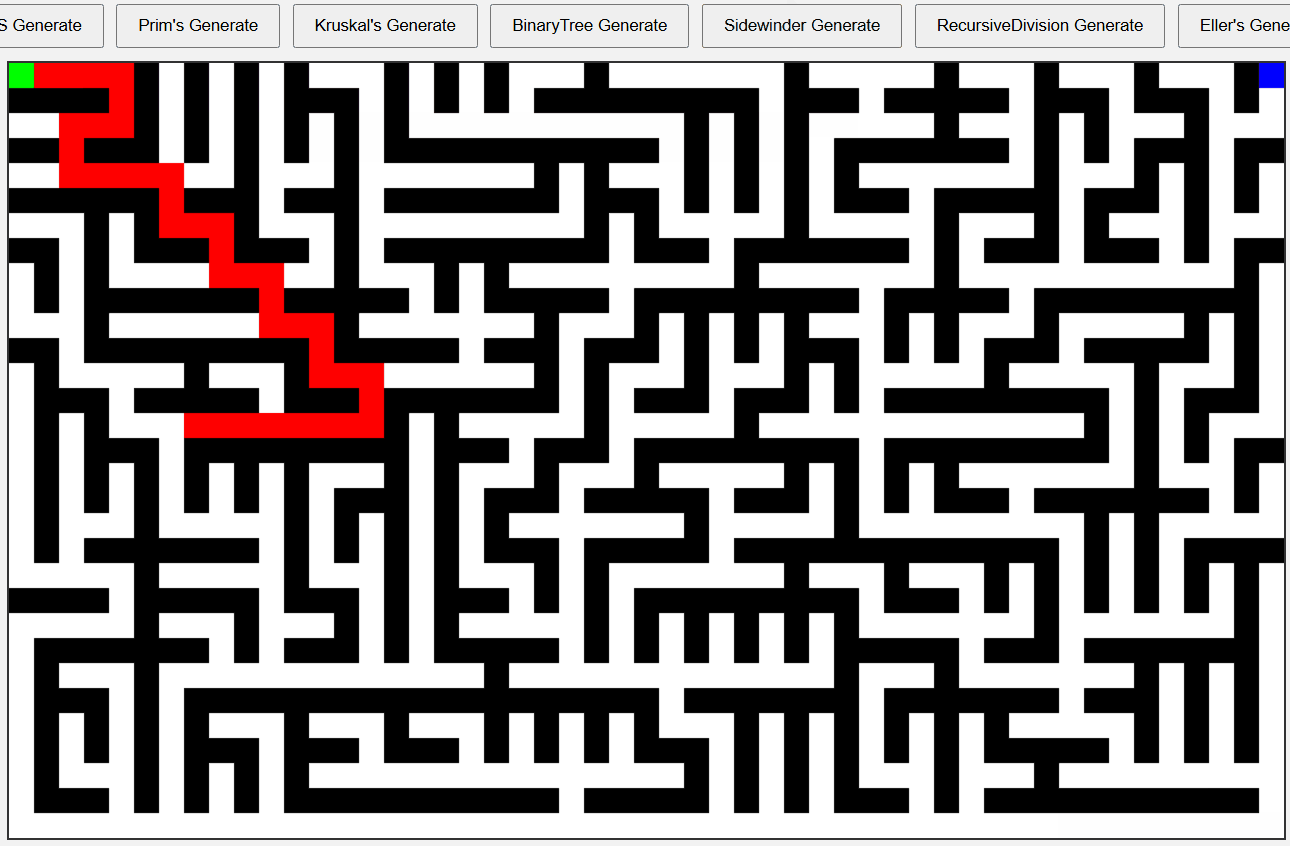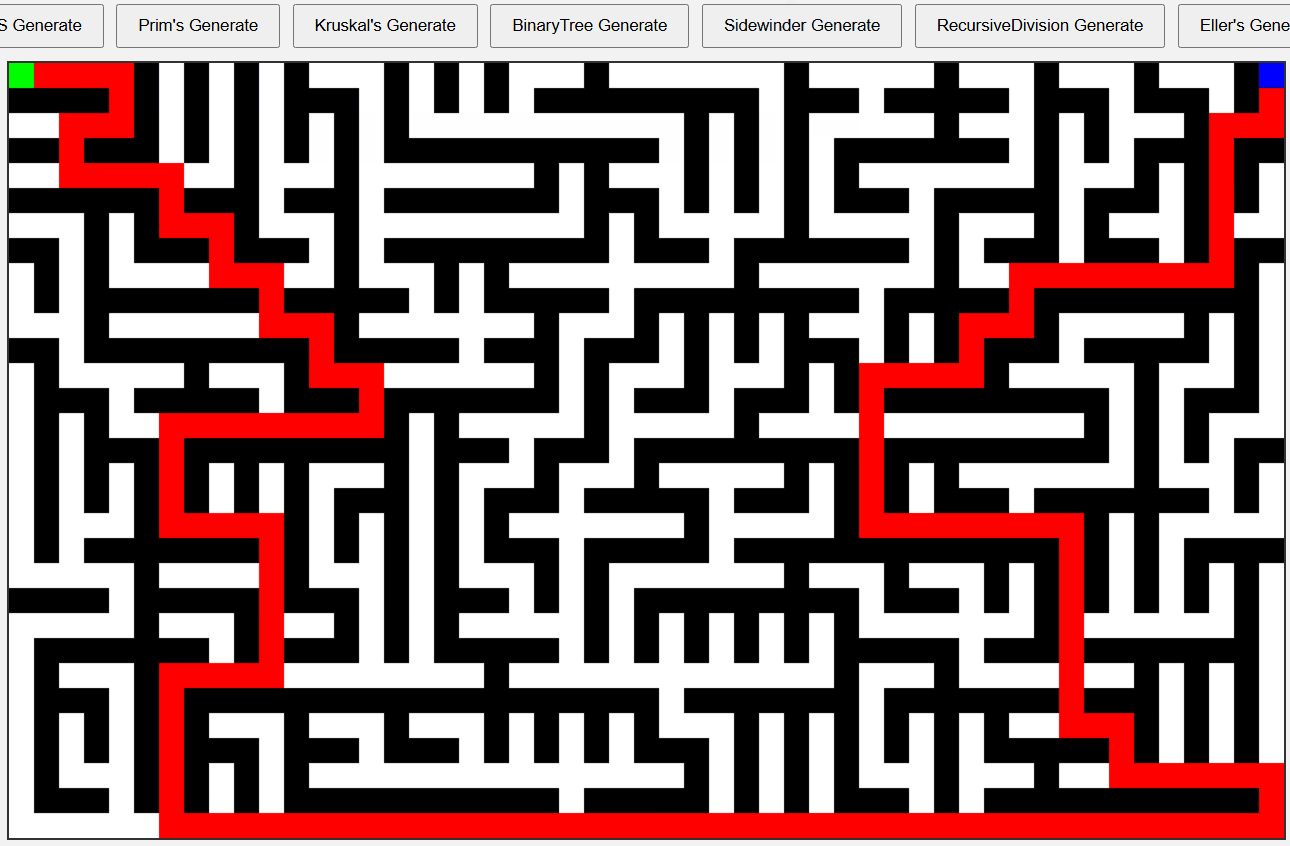
Binary Tree 알고리즘 미로
Sidewinder 알고리즘 미로
Recursive Division 알고리즘 미로
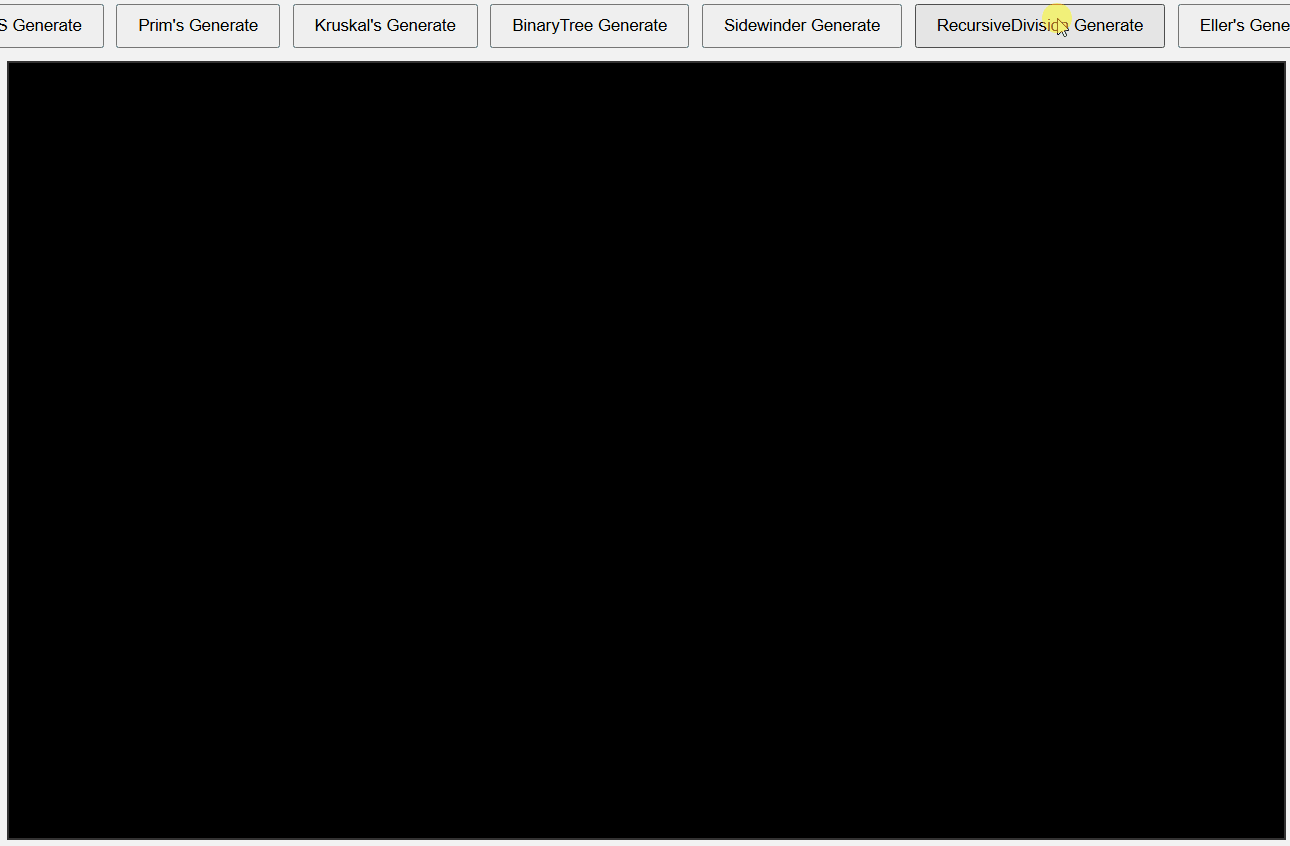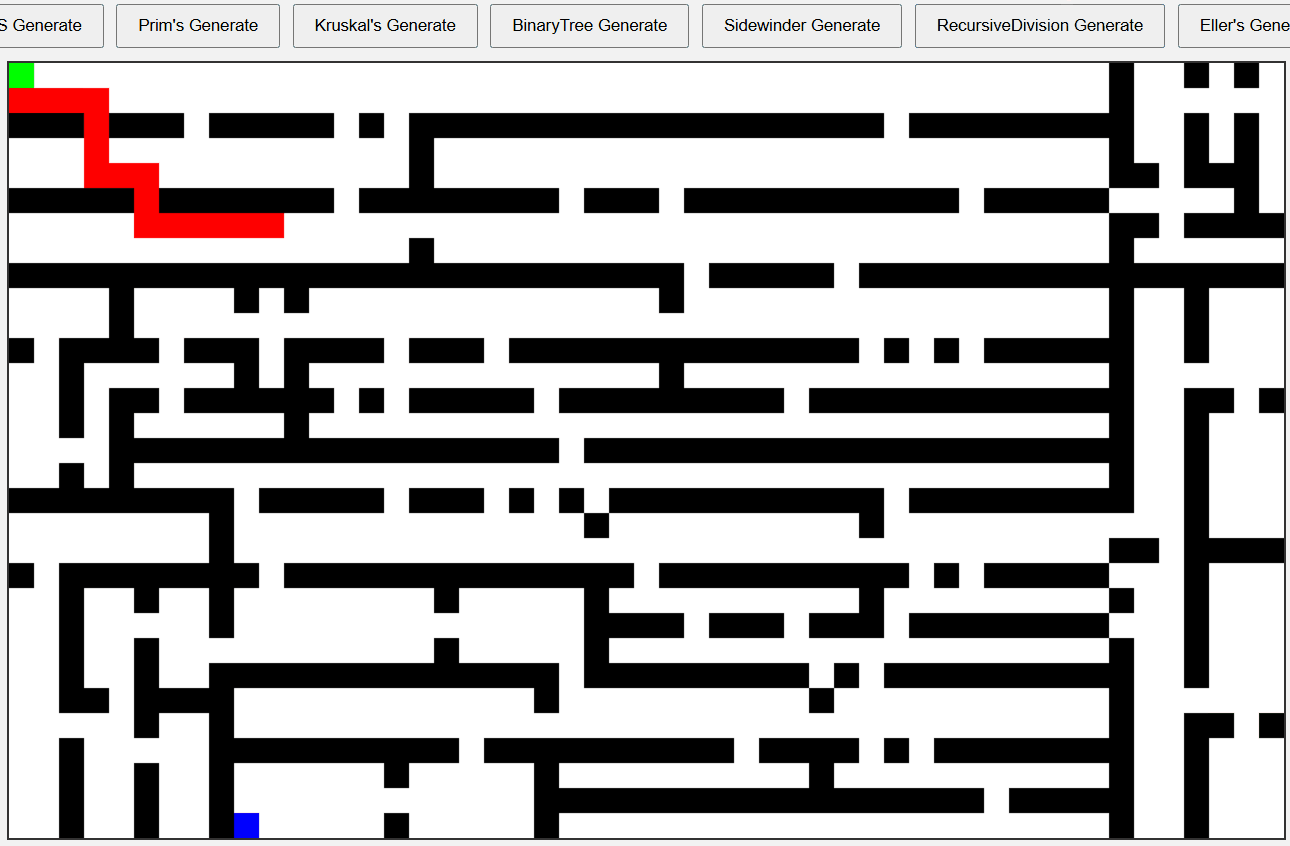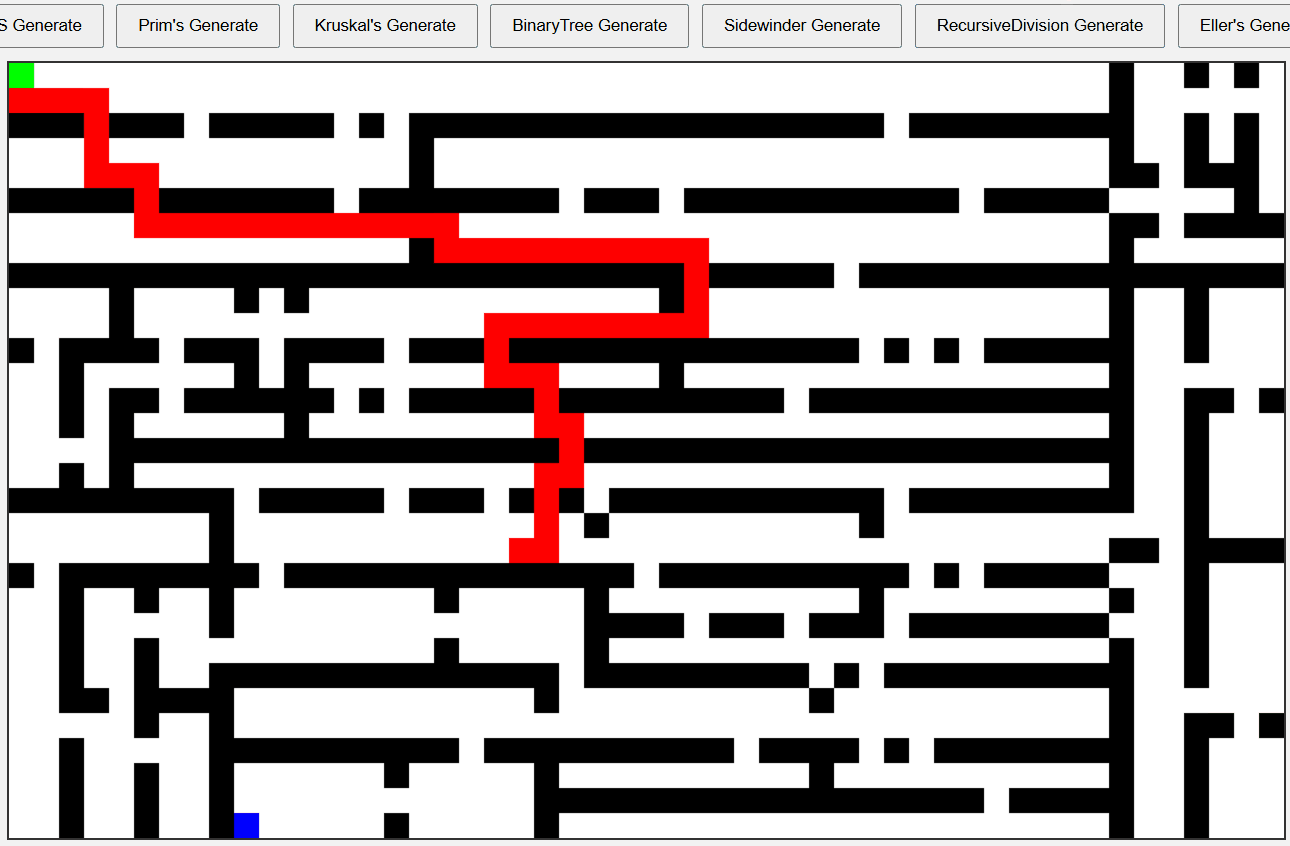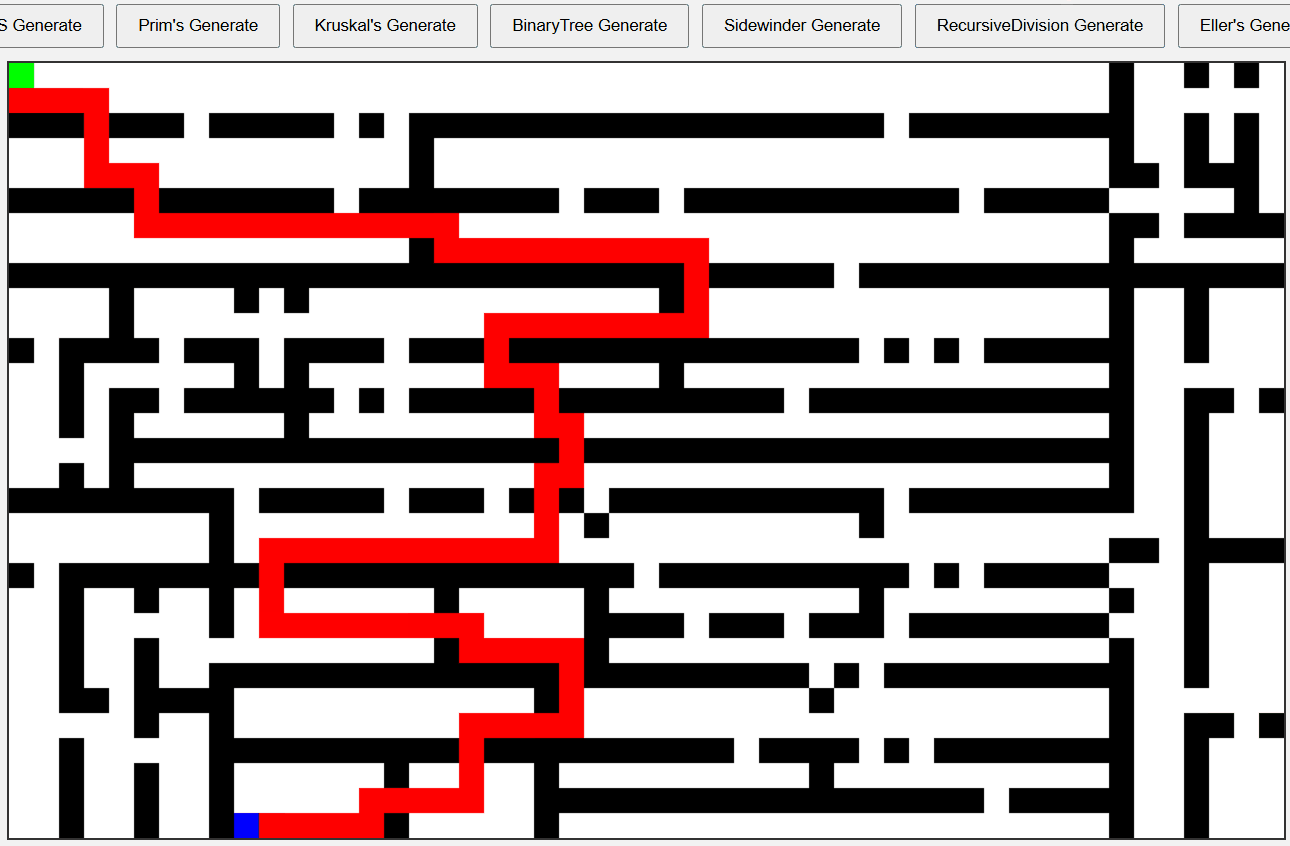
Eller’s 알고리즘 미로
반성
7종 알고리즘 미로를 완성했다.
그 외 몇가지 알고리즘이 더 있긴한데, 대표적으로 이 7종이면 더 맛 볼 필요는 없다고 한다.
그리고 미로 알고리즘 짜다가 알게 되었는데 던전 맵 만드는 알고리즘과 미로 알고리즘은 또 다르다고 한다…
정리 되면 던전 맵 시뮬레이터도 만들어봐야겠다.
코드 확인
Binary Tree
Link to GitHub
Sidewinder
Link to GitHub
Recursive Division
Link to GitHub
Eller’s
Link to GitHub